Payroll System: What It Is and How It Works

Payroll systems manage everything having to do with the process of paying employees and filing employment taxes. They are put in place to keep track of worked hours, calculating wages, calculating withholding taxes and other deductions, printing and delivering checks, and paying government employment taxes.
Software is often used for payroll and requires minimum input from employers. Employers are required to input wages and hours worked and then the software uses this information to automatically perform calculations and deduct withholdings. Most payroll system software is automatically updated when tax laws change and will alert employers when to file certain tax forms.
Table of Contents
- What Is The Payroll Process?
- 6 Reasons Payroll Systems Are Important
- How to Make Payroll System in Excel
What Is the Payroll Process?
A payroll administrator needs to do detailed planning of the whole payroll process. There is always work managing ongoing tasks that need attention and constant monitoring of changes to tax withholding, contribution, and other things to consider in the process.
The payroll process can be split into three stages — pre-payroll, actual payroll, and post payroll activities.
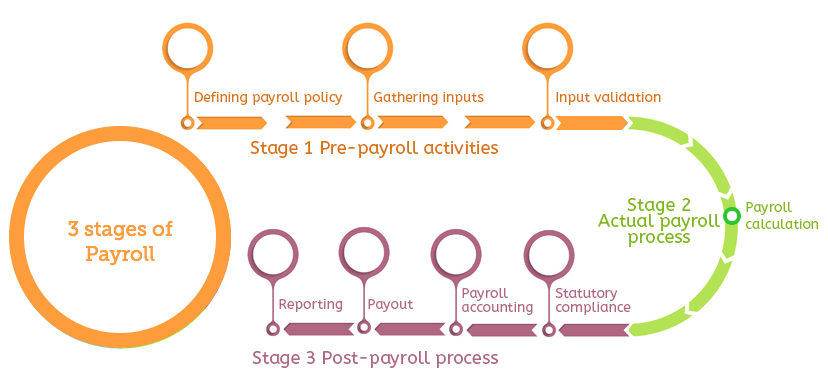
Pre-payroll Activities
Defining policy: In these beginning stages, it is important to establish a company’s policies such as a pay policy, leave and benefits policy and attendance policy.
Ensure that these policies are well-defined and signed off by your company’s management so that standard payroll processing can be established.
Gathering input data: Interacting with multiple departments and payroll is often an integral part of the payroll process. These are the people who can give you more access to important information like mid-year salary revisions and attendance data.
The process might be more consolidated in smaller organizations and more robust in larger companies. Gathering this data can be overwhelming but payroll software has integrated features like leave and attendance management and employee self-service portals to make the job easier.
Input validation: The next step in the process is checking the validity of the input data and whether it adheres to company policy. This is the time to make sure no active employee has been missed and no inactive employee has been included in the salary payment.
Actual Payroll Process
Payroll calculation: This is the stage in the payroll process where input data is put into the payroll system to actually process the payroll. This process results in net pay being generated after adjusting necessary taxes and deductions.
After this process is complete, it is best practice to reconcile the values and verify accuracy to avoid errors.

Post-payroll Process
Statutory compliance: At the time of processing all statutory deductions like EPF (Employee Provident Fund), TDS (Tax Deduction at Source), and ESI (Employee State Insurance) are deducted. The payroll administrator then sends the amount to the appropriate government agencies.
The frequency of this process can vary depending on the dues. Most of these fees can be made through specific forms set in place. After all the dues are paid, return reports are filed.
Payroll accounting: It is important that every organization keep a record of all its financial transactions for the payroll process.
Salaries are one of the most vital parts of operating costs to be recorded in your book of accounts. Payroll management should always ensure that all salary and reimbursement data is accurately entered into the company’s accounting or ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system.
Payout: Salaries can be paid out by cash, check, or bank transfer. Typically, employers deposit salaries directly into an employee’s bank account.
Once payroll is processed, a company needs to ensure its bank account has enough funds to make salary payments.
The next step is getting a salary bank advice statement from the company’s branch. This statement includes details like employee id, bank account number, and amount of wages.
If you’re using payroll software that has an employee self-serve portal, it will be easier to publish payslips and employees can log in to access their account and payslips.
Reporting: After you’ve completed payroll for a particular month, your finance department or management team might ask for a report on things like department employee costs or location employee costs.
A payroll administrator will need to gather the data and extract the required information to share these reports.
6 Reasons Payroll Systems Are Important
Payroll is an integral part of a company’s operations. Not only is it responsible for employees’ salary compensation but it also plays an important role in protecting a company by ensuring it is following compliance with tax legislation.
Here are other reasons payroll systems are so important:
1) Employee Morale
An important part of keeping employees happy is paying them on time.
Ensuring that you have a payroll system that pays your company in a timely manner on a consistent basis will definitely impact your employee morale. Late and inaccurate payment is likely to cause your employees to question the financial stability of the company. This might affect the overall environment and culture of your company, resulting in a negative attitude from employees that could bleed into their day-to-day tasks and cause underperformance.
A company’s workforce is often the heart of a company and a reliable and accurate payroll is part of what keeps that heart beating.
2) Compensation
Payroll goes beyond an employee’s salary.
An employee’s compensation can also include bonuses and benefits on top of their salary. Bonuses and salary increases associated with performance evaluations are also managed through the payroll system.
3) Reputation
Not only does a company have a financial obligation to its employees, but it must also ensure that its payroll activities are compliant with the country’s tax and employment legislation.
Following legislative laws and efficiently meeting tax obligations establishes a company as a stable employer. This boost to a company’s reputation will ultimately attract and retain a solid pool of talent.
4) Government Reporting
A payroll system helps companies comply with tax and employment legislation.
A company needs to report its payroll tax withholdings, payments, and employee statuses to local, state, and federal governments on a quarterly or annual basis. Your company’s requirements often depend on the size of your payroll and the type of business you are running.
5) Following Labor Laws
Understanding labor compliance is another way to make sure your company has happy employees and is following local and federal laws.
Each state has different labor laws regarding minimum wage, overtime, labor law posters, termination procedures, and more. Payroll systems and payroll administrators make those rules easier to follow and understand.
6) Paying Taxes
To follow state and federal tax laws, companies need to withhold income and payroll taxes from an employee’s payroll and pay those taxes on time.
Employers often cover the costs of employees’ benefits and a portion of that might come from an employee’s gross wage. A company’s payroll system also needs to deduct Social Security and Medicare payments from an employee’s gross wages. On most payrolls, an employer’s payroll system will withhold federal and state income taxes from an employee’s payroll.

How to Make a Payroll System in Excel
Creating a manual payroll calculator can be tedious but Microsoft has a free payroll calculator template for Excel for both Windows and Mac computers. There is also software that can be used to automate your payroll and make your life much easier.
Here are instructions on how to use this tool.
- Go to https://templates.office.com/en-us/Payroll-calculator-TM06101177
- Download
- Open template in Microsoft Excel
- Under the Employee Information Tab add employee information
- Determine your employees’ payroll on Payroll Calculator Tab
RELATED ARTICLES
 How to Make Adjusting Entries
How to Make Adjusting Entries How to Correct Accounting Errors—and 7 of the Most Common Types
How to Correct Accounting Errors—and 7 of the Most Common Types Single Entry System Accounting: an Introduction
Single Entry System Accounting: an Introduction What Are Accrued Expenses? Definition and Examples
What Are Accrued Expenses? Definition and Examples What Is a Deferral? It’s Expenses Prepaid or Revenue Not yet Earned
What Is a Deferral? It’s Expenses Prepaid or Revenue Not yet Earned Cloud Accounting: What It Is, How It Works And Its Benefits
Cloud Accounting: What It Is, How It Works And Its Benefits